TemporAI:医学时间序列的以机器学习为中心的工具包
项目描述
 TemporAI
TemporAI
⚗️ 状态: 此项目仍处于 alpha 状态,API可能会在没有警告的情况下更改。
📃 概述
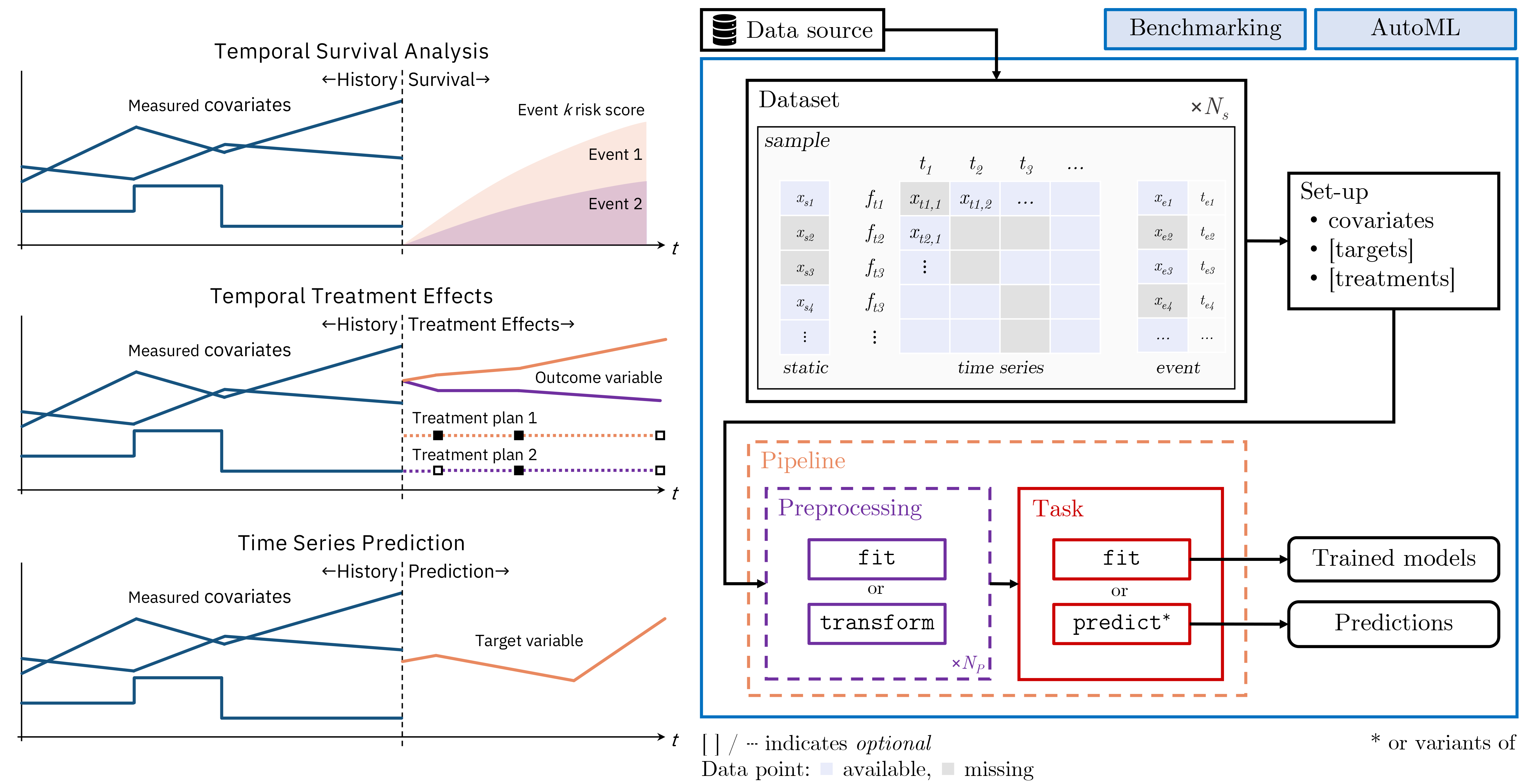
TemporAI 是一个针对医学的以机器学习为中心的时间序列库。TemporAI当前关注的任务包括:时间到事件(生存)分析、时间序列数据中的治疗效应(因果推断)和时间序列预测。提供数据预处理方法,包括静态和时间协变量的缺失值填充。还提供用于超参数调整和管道选择的AutoML工具。
TemporAI的独特之处在哪里?
- 🏥 药物优先: 专注于药物和医疗保健的应用案例,例如时间治疗效应、随时间进行的生存分析、插补方法、内置和事后可解释性的模型等。参见 方法。
- 🏗️ 快速原型设计: 一种插件设计,允许用户即时集成新方法。
- 🚀 从研究到实践: 研究社区中相关的创新模型,适用于实际应用。
- 🌍 医疗保健生态系统愿景: 计划一系列交互式演示应用、新的医学问题设置、可解释性工具、以数据为中心的工具等。
关键概念
🚀 安装
使用 pip 安装
$ pip install temporai
或从源代码安装
$ git clone https://github.com/vanderschaarlab/temporai.git
$ cd temporai
$ pip install .
在 conda 环境中安装
尽管TemporAI尚未发布到 conda-forge,您仍然可以使用以下方式在您的conda环境中使用pip安装TemporAI
按常规创建和激活conda环境
$ conda create -n <my_environment>
$ conda activate <my_environment>
然后在您的conda环境中使用pip进行安装
$ pip install temporai
💥 示例用法
- 列出可用的插件
from tempor import plugin_loader
print(plugin_loader.list())
- 使用时间至事件(生存)分析模型
from tempor import plugin_loader
# Load a time-to-event dataset:
dataset = plugin_loader.get("time_to_event.pbc", plugin_type="datasource").load()
# Initialize the model:
model = plugin_loader.get("time_to_event.dynamic_deephit")
# Train:
model.fit(dataset)
# Make risk predictions:
prediction = model.predict(dataset, horizons=[0.25, 0.50, 0.75])
- 使用时间治疗效应模型
import numpy as np
from tempor import plugin_loader
# Load a dataset with temporal treatments and outcomes:
dataset = plugin_loader.get(
"treatments.temporal.dummy_treatments",
plugin_type="datasource",
temporal_covariates_missing_prob=0.0,
temporal_treatments_n_features=1,
temporal_treatments_n_categories=2,
).load()
# Initialize the model:
model = plugin_loader.get("treatments.temporal.regression.crn_regressor", epochs=20)
# Train:
model.fit(dataset)
# Define target variable horizons for each sample:
horizons = [
tc.time_indexes()[0][len(tc.time_indexes()[0]) // 2 :] for tc in dataset.time_series
]
# Define treatment scenarios for each sample:
treatment_scenarios = [
[np.asarray([1] * len(h)), np.asarray([0] * len(h))] for h in horizons
]
# Predict counterfactuals:
counterfactuals = model.predict_counterfactuals(
dataset,
horizons=horizons,
treatment_scenarios=treatment_scenarios,
)
- 使用缺失数据插补器
from tempor import plugin_loader
dataset = plugin_loader.get(
"prediction.one_off.sine", plugin_type="datasource", with_missing=True
).load()
static_data_n_missing = dataset.static.dataframe().isna().sum().sum()
temporal_data_n_missing = dataset.time_series.dataframe().isna().sum().sum()
print(static_data_n_missing, temporal_data_n_missing)
assert static_data_n_missing > 0
assert temporal_data_n_missing > 0
# Initialize the model:
model = plugin_loader.get("preprocessing.imputation.temporal.bfill")
# Train:
model.fit(dataset)
# Impute:
imputed = model.transform(dataset)
temporal_data_n_missing = imputed.time_series.dataframe().isna().sum().sum()
print(static_data_n_missing, temporal_data_n_missing)
assert temporal_data_n_missing == 0
- 使用一次性分类器(预测)
from tempor import plugin_loader
dataset = plugin_loader.get("prediction.one_off.sine", plugin_type="datasource").load()
# Initialize the model:
model = plugin_loader.get("prediction.one_off.classification.nn_classifier", n_iter=50)
# Train:
model.fit(dataset)
# Predict:
prediction = model.predict(dataset)
- 使用时间回归器(预测)
from tempor import plugin_loader
# Load a dataset with temporal targets.
dataset = plugin_loader.get(
"prediction.temporal.dummy_prediction",
plugin_type="datasource",
temporal_covariates_missing_prob=0.0,
).load()
# Initialize the model:
model = plugin_loader.get("prediction.temporal.regression.seq2seq_regressor", epochs=10)
# Train:
model.fit(dataset)
# Predict:
prediction = model.predict(dataset, n_future_steps=5)
- 基准模型,时间至事件任务
from tempor.benchmarks import benchmark_models
from tempor import plugin_loader
from tempor.methods.pipeline import pipeline
testcases = [
(
"pipeline1",
pipeline(
[
"preprocessing.scaling.temporal.ts_minmax_scaler",
"time_to_event.dynamic_deephit",
]
)({"ts_coxph": {"n_iter": 100}}),
),
(
"plugin1",
plugin_loader.get("time_to_event.dynamic_deephit", n_iter=100),
),
(
"plugin2",
plugin_loader.get("time_to_event.ts_coxph", n_iter=100),
),
]
dataset = plugin_loader.get("time_to_event.pbc", plugin_type="datasource").load()
aggr_score, per_test_score = benchmark_models(
task_type="time_to_event",
tests=testcases,
data=dataset,
n_splits=2,
random_state=0,
horizons=[2.0, 4.0, 6.0],
)
print(aggr_score)
- 序列化
from tempor.utils.serialization import load, save
from tempor import plugin_loader
# Initialize the model:
model = plugin_loader.get("prediction.one_off.classification.nn_classifier", n_iter=50)
buff = save(model) # Save model to bytes.
reloaded = load(buff) # Reload model.
# `save_to_file`, `load_from_file` also available in the serialization module.
- AutoML - 寻找最佳管道
from tempor.automl.seeker import PipelineSeeker
dataset = plugin_loader.get("prediction.one_off.sine", plugin_type="datasource").load()
# Specify the AutoML pipeline seeker for the task of your choice, providing candidate methods,
# metric, preprocessing steps etc.
seeker = PipelineSeeker(
study_name="my_automl_study",
task_type="prediction.one_off.classification",
estimator_names=[
"cde_classifier",
"ode_classifier",
"nn_classifier",
],
metric="aucroc",
dataset=dataset,
return_top_k=3,
num_iter=100,
tuner_type="bayesian",
static_imputers=["static_tabular_imputer"],
static_scalers=[],
temporal_imputers=["ffill", "bfill"],
temporal_scalers=["ts_minmax_scaler"],
)
# The search will return the best pipelines.
best_pipelines, best_scores = seeker.search() # doctest: +SKIP
📖 教程
数据
用户指南
扩展TemporAI
- 编写自定义方法插件
- 测试自定义方法插件
- 编写自定义数据源插件
- 编写自定义度量插件
- 编写自定义数据格式
📘 文档
请查看完整的项目文档这里。
🌍 TemporAI 生态系统(实验性)
我们在 TemporAI 生态系统中提供额外的工具,这些工具正在积极开发中,目前处于(非常)实验阶段。欢迎提出建议和贡献!
这些包括
temporai-clinic:一个用于交互和可视化 TemporAI 模型、数据和预测的 Web 应用工具。temporai-mivdp:为 TemporAI 定制的MIMIC-IV 数据管道。
🔑 方法
随时间进行的生存分析
根据事件数据进行风险估计(类别:time_to_event)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
dynamic_deephit |
Dynamic-DeepHit 通过包含各种重复测量的纵向数据(而不仅仅是最后可用的测量)来提供动态更新的生存预测。 | 论文 |
ts_coxph |
从时间序列创建嵌入,并使用 CoxPH 模型预测生存函数 | --- |
ts_xgb |
从时间序列创建嵌入,并使用 SurvivalXGBoost 模型预测生存函数 | --- |
治疗效应
一次性
在治疗是一次性事件的情况下估计治疗效应。
- 对结果进行回归(类别:
treatments.one_off.regression)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
synctwin_regressor |
SyncTwin 是一种针对具有纵向数据的观察性研究的治疗效应估计方法,适用于 LIP 设置:纵向、不规律和点治疗。 | 论文 |
时间
在治疗是时间序列的情况下估计治疗效应。
- 对结果进行分类(类别:
treatments.temporal.classification)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
crn_classifier |
Counterfactual Recurrent Network (CRN),一个序列到序列模型,利用可用的患者观察数据来估计随时间变化的治疗效应。 | 论文 |
- 对结果进行回归(类别:
treatments.temporal.regression)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
crn_regressor |
Counterfactual Recurrent Network (CRN),一个序列到序列模型,利用可用的患者观察数据来估计随时间变化的治疗效应。 | 论文 |
预测
一次性
当目标是静态时进行预测。
- 分类(类别:
prediction.one_off.classification)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
nn_classifier |
基于神经网络的分类器。支持多种循环模型,如 RNN、LSTM、Transformer 等。 | --- |
ode_classifier |
基于常微分方程(ODE)求解器的分类器。 | --- |
cde_classifier |
用于不规则时间序列的基于神经网络控制的微分方程(Neural Controlled Differential Equations)的分类器。 | 论文 |
laplace_ode_classifier |
基于 PyTorch 实现的逆拉普拉斯变换(ILT)算法的分类器。 | 论文 |
- 回归(类别:
prediction.one_off.regression)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
nn_regressor |
基于神经网络的回归器。支持多种循环模型,如 RNN、LSTM、Transformer 等。 | --- |
ode_regressor |
基于常微分方程(ODE)求解器的回归器。 | --- |
cde_regressor |
用于不规则时间序列的基于神经网络控制的微分方程(Neural Controlled Differential Equations)的回归器。 | 论文 |
laplace_ode_regressor |
基于 PyTorch 实现的逆拉普拉斯变换(ILT)算法的回归器。 | 论文 |
时间
当目标是时间序列时进行预测。
- 分类(类别:
prediction.temporal.classification)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
seq2seq_classifier |
Seq2Seq 预测,分类 | --- |
- 回归(类别:
prediction.temporal.regression)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
seq2seq_regressor |
Seq2Seq 预测,回归 | --- |
预处理
特征编码
- 静态数据(类别:
preprocessing.encoding.static)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
static_onehot_encoder |
对类别静态特征进行 one-hot 编码 | --- |
- 时间数据(类别:
preprocessing.encoding.temporal)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
ts_onehot_encoder |
对类别时间序列特征进行 one-hot 编码 | --- |
插补
- 静态数据(类别:
preprocessing.imputation.static)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
static_tabular_imputer |
使用来自 HyperImpute(HyperImpute、均值、中位数、最频繁、MissForest、ICE、MICE、SoftImpute、EM、Sinkhorn、GAIN、MIRACLE、MIWAE)的任何方法来填充静态数据 | 论文 |
- 时间数据(类别:
preprocessing.imputation.temporal)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
ffill |
将最后一个有效观测值向前传播到下一个有效值 | --- |
bfill |
使用下一个有效观测值来填充空缺 | --- |
ts_tabular_imputer |
使用来自 HyperImpute(HyperImpute、均值、中位数、最频繁、MissForest、ICE、MICE、SoftImpute、EM、Sinkhorn、GAIN、MIRACLE、MIWAE)的任何方法来填充时间序列数据 | 论文 |
缩放
- 静态数据(类别:
preprocessing.scaling.static)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
static_standard_scaler |
使用StandardScaler缩放静态特征 | --- |
static_minmax_scaler |
使用MinMaxScaler缩放静态特征 | --- |
- 时间数据(类别:
preprocessing.scaling.temporal)
| 名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
ts_standard_scaler |
使用StandardScaler缩放时间特征 | --- |
ts_minmax_scaler |
使用MinMaxScaler缩放时间特征 | --- |
🔨 测试和开发
使用以下命令安装测试依赖项
pip install .[testing]
可以使用以下命令执行测试
pytest -vsx
对于本地开发,我们建议您安装包含 [testing] 和一些额外依赖项的 [dev] 额外内容
pip install .[dev]
有关为 TemporAI 开发和贡献的详细信息,请参阅
- 📓 扩展 TemporAI 教程
- 📃 贡献指南
- 👩💻 开发者指南
✍️ 引用
如果您使用此代码,请引用相关论文
@article{saveliev2023temporai,
title={TemporAI: Facilitating Machine Learning Innovation in Time Domain Tasks for Medicine},
author={Saveliev, Evgeny S and van der Schaar, Mihaela},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.12260},
year={2023}
}
项目详情
下载文件
下载适合您平台的文件。如果您不确定选择哪个,请了解有关 安装包 的更多信息。
源分布
此版本没有可用的源分布文件。有关生成分布存档的教程,请参阅 生成分布存档。
构建分布
temporai-0.0.3-py3-none-any.whl (236.6 kB 查看哈希值)