一个用于在Python中处理Table Schema的实用库
项目描述
tableschema-py
Table Schema标准的Python实现。
[重要通知] 我们已经发布了 Frictionless Framework。此框架提供了改进的
tableschema功能,扩展为完整的数据解决方案。该变更不会破坏现有软件,因此无需采取任何操作。请阅读从tableschema到 Frictionless Framework 的迁移指南。
功能
Table用于处理由 Table Schema 描述的数据表Schema表示 Table SchemaField表示 Table Schema 字段validate用于验证 Table Schemainfer用于从数据推断 Table Schema- 内置命令行界面以验证和推断模式
- 存储/插件系统将表连接到不同的存储后端,如 SQL 数据库
内容
入门指南
安装
该包使用语义版本控制。这意味着主版本可能包括破坏性更改。强烈建议在您的 setup/requirements 文件中指定 tableschema 版本范围,例如 tableschema>=1.0,<2.0。
$ pip install tableschema
文档
简介
让我们从一个简单的例子开始
from tableschema import Table
# Create table
table = Table('path.csv', schema='schema.json')
# Print schema descriptor
print(table.schema.descriptor)
# Print cast rows in a dict form
for keyed_row in table.iter(keyed=True):
print(keyed_row)
处理表
在表格数据世界中,表是一个核心概念。它通过元数据(Table Schema)表示数据。让我们看看我们如何在实践中使用它。
假设我们有一些本地的 csv 文件。它可以是内联数据或来自远程链接——所有这些都由 Table 类支持(当然,除了用于浏览器内使用的本地文件)。但现在假设它是 data.csv
city,location
london,"51.50,-0.11"
paris,"48.85,2.30"
rome,N/A
让我们创建并读取一个表实例。我们使用静态的 Table.load 方法以及带有 keyed 选项的 table.read 方法来获取键行数组
table = Table('data.csv')
table.headers # ['city', 'location']
table.read(keyed=True)
# [
# {city: 'london', location: '51.50,-0.11'},
# {city: 'paris', location: '48.85,2.30'},
# {city: 'rome', location: 'N/A'},
# ]
正如我们所看到的,我们的位置只是字符串。但它们应该是地理点。罗马的位置不可用,但只是一个字符串 N/A 而不是 None。首先,我们必须推断 Table Schema
table.infer()
table.schema.descriptor
# { fields:
# [ { name: 'city', type: 'string', format: 'default' },
# { name: 'location', type: 'geopoint', format: 'default' } ],
# missingValues: [ '' ] }
table.read(keyed=True)
# Fails with a data validation error
让我们修复“不可用”的位置。Table Schema 规范中有一个 missingValues 属性。作为第一次尝试,我们在 table.schema.descriptor 中将 missingValues 设置为 N/A。模式描述符可以就地更改,但所有更改都应使用 table.schema.commit() 提交
table.schema.descriptor['missingValues'] = 'N/A'
table.schema.commit()
table.schema.valid # false
table.schema.errors
# [<ValidationError: "'N/A' is not of type 'array'">]
作为好公民,我们决定检查我们的模式描述符的有效性。但它是无效的!我们应该为 missingValues 属性使用数组。此外,别忘了包括“空字符串”作为有效的缺失值
table.schema.descriptor['missingValues'] = ['', 'N/A']
table.schema.commit()
table.schema.valid # true
一切都很好。看起来我们准备好再次读取我们的数据了
table.read(keyed=True)
# [
# {city: 'london', location: [51.50,-0.11]},
# {city: 'paris', location: [48.85,2.30]},
# {city: 'rome', location: null},
# ]
现在我们看到
- 位置是包含数值纬度和经度的数组
- 罗马的位置是原生的 Python
None
由于读取后没有错误,我们可以确信我们的数据与我们的模式有效。让我们保存它
table.schema.save('schema.json')
table.save('data.csv')
我们的 data.csv 看起来是一样的,因为它被字符串化为 csv 格式。但现在我们有了 schema.json
{
"fields": [
{
"name": "city",
"type": "string",
"format": "default"
},
{
"name": "location",
"type": "geopoint",
"format": "default"
}
],
"missingValues": [
"",
"N/A"
]
}
如果我们决定进一步改进它,我们可以更新模式文件,然后再次打开它。但现在提供模式路径
table = Table('data.csv', schema='schema.json')
# Continue the work
如前所述,给定的模式可以用于 验证 数据(有关模式规范详细信息的说明,请参阅模式部分)。在默认模式下,无效数据行会立即在 table.iter()/table.write() 方法中触发 异常。
假设这个模式无效的本地文件 invalid_data.csv
key,value
zero,0
one,not_an_integer
two,2
我们将验证数据是否符合以下模式
table = Table(
'invalid_data.csv',
schema={'fields': [{'name': 'key'}, {'name': 'value', 'type': 'integer'}]})
遍历数据时,由于将 'not_an_integer' 转换为 int 失败,引发异常
for row in table.iter():
print(row)
# Traceback (most recent call last):
# ...
# tableschema.exceptions.CastError: There are 1 cast errors (see exception.errors) for row "3"
提示:行号计数从 1 开始,包括标题行。
(注:您可以选择禁用使用 cast 参数的 iter()/read() 值转换,请参阅以下参考。)
通过为这些方法提供自定义异常处理器(可调用的对象),您可以自行处理发生的异常,例如“延迟失败”,例如收集整个数据的验证报告
errors = []
def exc_handler(exc, row_number=None, row_data=None, error_data=None):
errors.append((exc, row_number, row_data, error_data))
for row in table.iter(exc_handler=exc_handler):
print(row)
# ['zero', 0]
# ['one', FailedCast('not_an_integer')]
# ['two', 2]
print(errors)
# [(CastError('There are 1 cast errors (see exception.errors) for row "3"',),
# 3,
# OrderedDict([('key', 'one'), ('value', 'not_an_integer')]),
# OrderedDict([('value', 'not_an_integer')]))]
注意:
- 即使数据模式无效,也会产生数据行;这是因为我们的自定义表达式处理器选择不抛出异常(而是将它们收集在错误列表中)。
- 无法正确转换的数据字段值(如果
iter()/read()cast 参数设置为 True,这是默认值),将被包裹在FailedCast“值持有者” 中。这允许在数据消费者侧区分未转换的值和成功转换的值。FailedCast实例只能在自定义异常处理的情况下产生。 - 自定义异常处理器可调用对象必须支持
iter()/read()部分的Table类 API 参考中指定的函数签名。
处理模式
一个具有处理模式和支持数据的辅助方法的模式模型。模式实例可以用模式源作为 JSON 文件的 URL 或 JSON 对象来初始化。模式最初是经过验证的(见下文 validate)。默认情况下,验证错误将存储在 schema.errors 中,但在严格模式下会立即抛出。
让我们创建一个空白模式。它无效,因为 descriptor.fields 属性是 Table Schema 规范所要求的
schema = Schema()
schema.valid # false
schema.errors
# [<ValidationError: "'fields' is a required property">]
为了避免手动创建模式描述符,我们将使用 schema.infer 方法从给定的数据推断描述符
schema.infer([
['id', 'age', 'name'],
['1','39','Paul'],
['2','23','Jimmy'],
['3','36','Jane'],
['4','28','Judy'],
])
schema.valid # true
schema.descriptor
#{ fields:
# [ { name: 'id', type: 'integer', format: 'default' },
# { name: 'age', type: 'integer', format: 'default' },
# { name: 'name', type: 'string', format: 'default' } ],
# missingValues: [ '' ] }
现在我们有一个推断的模式,它有效。我们可以将数据行与我们的模式进行转换。我们提供一个字符串输入,它将被相应地转换
schema.cast_row(['5', '66', 'Sam'])
# [ 5, 66, 'Sam' ]
但是,如果我们尝试向 age 字段提供一些缺失值,转换将失败,因为唯一有效的“缺失”值是一个空字符串。让我们更新我们的模式
schema.cast_row(['6', 'N/A', 'Walt'])
# Cast error
schema.descriptor['missingValues'] = ['', 'N/A']
schema.commit()
schema.cast_row(['6', 'N/A', 'Walt'])
# [ 6, None, 'Walt' ]
我们可以将模式保存到本地文件,并随时通过从该文件加载它来继续在该模式上工作
schema.save('schema.json')
schema = Schema('schema.json')
处理字段
from tableschema import Field
# Init field
field = Field({'name': 'name', 'type': 'number'})
# Cast a value
field.cast_value('12345') # -> 12345
可以使用 Field 实例将数据值转换为原生 Python 对象。Type 实例可以用 字段描述符 初始化。这允许定义格式和约束。
转换值将检查该值是否为预期的类型,是否处于正确的格式,并且是否符合模式施加的任何约束。例如,可以使用 DateType 实例来转换日期值(在 ISO 8601 格式中)。无法转换的值将引发 InvalidCastError 异常。
不符合约束的值将引发 ConstraintError 异常。
API 参考
cli
cli()
命令行界面
Usage: tableschema [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Options:
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
infer Infer a schema from data.
info Return info on this version of Table Schema
validate Validate that a supposed schema is in fact a Table Schema.
Table
Table(self,
source,
schema=None,
strict=False,
post_cast=[],
storage=None,
**options)
表表示
参数
- source (str/list[]):数据源,以下之一
- 本地文件(路径)
- 远程文件(URL)
- 表示行的数组的数组
- schema (any):数据模式,以
Schema类支持的所有形式 - strict (bool):传递给
Schema构造函数的严格性选项 - post_cast (function[]):后转换处理器列表
- storage (None):存储名称,如
sql或bigquery - options (dict):tabulator 或存储的选项
引发
TableSchemaException:在发生任何错误时引发
table.hash
如果可用,表的 SHA256 哈希。
如果已通过例如 table.read 读取,否则返回 None。在迭代过程中,返回已读取内容的哈希值
返回
str/None:SHA256 哈希
table.headers
表头可用
返回
str[]:表头
table.schema
如果可用,返回模式类实例
返回
Schema:模式
table.size
如果可用,以字节为单位的表大小
如果已通过例如 table.read 读取,否则返回 None。在迭代过程中,返回已读取内容的大小
返回
int/None:字节大小
table.iter
table.iter(keyed=False,
extended=False,
cast=True,
integrity=False,
relations=False,
foreign_keys_values=False,
exc_handler=None)
遍历表数据,并基于表模式发射行。
参数
keyed (bool):
yield keyed rows in a form of `{header1: value1, header2: value2}`
(default is false; the form of rows is `[value1, value2]`)
extended (bool):
yield extended rows in a for of `[rowNumber, [header1, header2], [value1, value2]]`
(default is false; the form of rows is `[value1, value2]`)
cast (bool):
disable data casting if false
(default is true)
integrity (dict):
dictionary in a form of `{'size': <bytes>, 'hash': '<sha256>'}`
to check integrity of the table when it's read completely.
Both keys are optional.
relations (dict):
dictionary of foreign key references in a form
of `{resource1: [{field1: value1, field2: value2}, ...], ...}`.
If provided, foreign key fields will checked and resolved
to one of their references (/!\ one-to-many fk are not completely resolved).
foreign_keys_values (dict):
three-level dictionary of foreign key references optimized
to speed up validation process in a form of
`{resource1: {(fk_field1, fk_field2): {(value1, value2): {one_keyedrow}, ... }}}`.
If not provided but relations is true, it will be created
before the validation process by *index_foreign_keys_values* method
exc_handler (func):
optional custom exception handler callable.
Can be used to defer raising errors (i.e. "fail late"), e.g.
for data validation purposes. Must support the signature below
自定义异常处理程序
def exc_handler(exc, row_number=None, row_data=None, error_data=None):
'''Custom exception handler (example)
# Arguments:
exc(Exception):
Deferred exception instance
row_number(int):
Data row number that triggers exception exc
row_data(OrderedDict):
Invalid data row source data
error_data(OrderedDict):
Data row source data field subset responsible for the error, if
applicable (e.g. invalid primary or foreign key fields). May be
identical to row_data.
'''
# ...
引发
TableSchemaException:任何错误的基类CastError:数据转换错误IntegrityError:完整性检查错误UniqueKeyError:唯一键约束违规UnresolvedFKError:未解决的键引用错误
返回
Iterator[list]:产生行
table.read
table.read(keyed=False,
extended=False,
cast=True,
limit=None,
integrity=False,
relations=False,
foreign_keys_values=False,
exc_handler=None)
读取整个表,并以行数组的形式返回
它与
table.iter的 API 相同,除了
参数
- limit (int):限制要读取和返回的行数
返回
list[]:返回行
table.infer
table.infer(limit=100,
confidence=0.75,
missing_values=[''],
guesser_cls=None,
resolver_cls=None)
推断表的模式。
它将根据表数据推断并设置 table.schema 为表模式。
参数
- limit (int):限制行样本大小
- confidence (float):允许多少转换错误(作为比例,介于 0 和 1 之间)
- missing_values (str[]):缺失值列表(默认
['']) - guesser_cls (class):您可以通过提供类型猜测和类型解析类来实现推断策略 [实验性]
- resolver_cls (class):您可以通过提供类型猜测和类型解析类来实现推断策略 [实验性]
返回
dict:表模式描述符
table.save
table.save(target, storage=None, **options)
以逗号(,)分隔符在本地将数据源保存为 CSV 格式的文件
要保存模式,请使用
table.schema.save()
参数
- target (str):保存目标(例如文件路径)
- storage (None/str):存储名称,如
sql或bigquery - options (dict):
tabulator或存储选项
引发
TableSchemaException:如果存在保存问题,则引发错误
返回
True/Storage:返回 true 或存储实例
table.index_foreign_keys_values
table.index_foreign_keys_values(relations)
创建一个三级的字典,包含外键引用
我们创建了它们,以便优化验证过程的加速,形式为 {resource1: {(fk_field1, fk_field2): {(value1, value2): {one_keyedrow}, ... }}}。
对于模式中的每个外键,它将遍历相应的 relations['resource'] 来创建索引(即字典)现有外键字段的值,并为每个值组合存储在键行上。
此优化依赖于对单个外键可能值的索引,以加速后续的解析。
此方法为公共的,允许创建索引一次,然后应用于具有相同模式的多个表(典型情况下 grouped resources in datapackage)
注意
- 输出中的第二个键是外键字段的元组,作为外键的代理标识符
- 相同的关联资源可以被索引多次,因为模式可以包含多个指向同一资源的外键
参数
- relations (dict):外键引用的字典,形式为
{resource1: [{field1: value1, field2: value2}, ...], ...}。它必须包含所有在外键模式定义中指向的资源。
返回
dict:返回一个三层字典,用于优化外键引用,以加快验证过程,形式为 {resource1: {(fk_field1, fk_field2): {(value1, value2): {one_keyedrow}, ... }}})
Schema
Schema(self, descriptor={}, strict=False)
模式表示
参数
- descriptor (str/dict):模式描述符之一:- 本地路径 - 远程URL - 字典
- strict (bool):指定验证行为的标志:- 如果为false,则不会引发错误,而是收集在
schema.errors中 - 如果为true,则立即引发验证错误
引发
TableSchemaException:在过程中引发任何错误
schema.descriptor
模式描述符
返回
dict:描述符
schema.errors
验证错误
在严格模式下始终为空。
返回
Exception[]:验证错误
schema.field_names
模式字段名
返回
str[]:字段名数组
schema.fields
模式字段
返回
Field[]:字段实例数组
schema.foreign_keys
模式外键
返回
dict[]:外键
schema.headers
模式字段名
返回
str[]:字段名数组
schema.missing_values
模式缺失值
返回
str[]:缺失值
schema.primary_key
模式主键
返回
str[]:主键
schema.valid
验证状态
在严格模式下始终为true。
返回
bool:验证状态
schema.get_field
schema.get_field(name)
按名称获取模式字段。
如果想要修改字段描述符,请使用
table.update_field
参数
- name (str):模式字段名称
返回
Field/None:Field实例或未找到时为None
schema.get_field
schema.get_field(name)
按名称获取模式字段。
如果想要修改字段描述符,请使用
table.update_field
参数
- name (str):模式字段名称
返回
Field/None:Field实例或未找到时为None
schema.add_field
schema.add_field(descriptor)
向模式中添加新字段。
新模式描述符将与新添加的字段描述符进行验证。
参数
- descriptor (dict):字段描述符
引发
TableSchemaException:在过程中引发任何错误
返回
Field/None:添加的Field实例或未添加时为None
schema.update_field
schema.update_field(name, update)
按名称更新现有描述符字段
参数
- name (str):模式字段名称
- update (dict):应用于字段描述符的更新
返回
bool:成功时为true,如果没有找到要修改的字段,则为false
schema.remove_field
schema.remove_field(name)
按名称删除字段资源。
在删除字段描述符后,将验证模式描述符。
参数
- name (str):模式字段名称
引发
TableSchemaException:在过程中引发任何错误
返回
Field/None:删除的Field实例或未找到时为None
schema.cast_row
schema.cast_row(row, fail_fast=False, row_number=None, exc_handler=None)
根据字段类型和格式转换行。
参数
- row (any[]:数据行作为值数组的数组
返回
any[]:返回转换后的数据行
schema.infer
schema.infer(rows,
headers=1,
confidence=0.75,
guesser_cls=None,
resolver_cls=None)
根据数据样本推断并设置schema.descriptor。
参数
- rows (list[]):表示行的数组数组
- headers (int/str[]):数据样本标题(以下之一):- 包含标题的行号(
rows应包含标题行)- 标题数组(rows不应包含标题行) - confidence (float):允许多少转换错误(作为比例,介于 0 和 1 之间)
- guesser_cls (class):您可以通过提供类型猜测和类型解析类来实现推断策略 [实验性]
- resolver_cls (class):您可以通过提供类型猜测和类型解析类来实现推断策略 [实验性]
返回
dict:表模式描述符
schema.commit
schema.commit(strict=None)
如果描述符中有就地更改,则更新模式实例。
示例
from tableschema import Schema
descriptor = {'fields': [{'name': 'my_field', 'title': 'My Field', 'type': 'string'}]}
schema = Schema(descriptor)
print(schema.get_field('my_field').descriptor['type']) # string
# Update descriptor by field position
schema.descriptor['fields'][0]['type'] = 'number'
# Update descriptor by field name
schema.update_field('my_field', {'title': 'My Pretty Field'}) # True
# Change are not committed
print(schema.get_field('my_field').descriptor['type']) # string
print(schema.get_field('my_field').descriptor['title']) # My Field
# Commit change
schema.commit()
print(schema.get_field('my_field').descriptor['type']) # number
print(schema.get_field('my_field').descriptor['title']) # My Pretty Field
参数
- strict (bool):更改
strict模式以进行进一步工作
引发
TableSchemaException:在过程中引发任何错误
返回
bool:成功时为true,如果没有修改则为false
schema.save
schema.save(target, ensure_ascii=True)
将模式描述符保存到目标位置。
参数
- target (str):保存描述符的路径
引发
TableSchemaException:在过程中引发任何错误
返回
bool:成功时为true
Field
Field(self, descriptor, missing_values=[''], schema=None)
字段表示
参数
- descriptor (dict):模式字段描述符
- missingValues (str[]):表示缺失值的字符串数组
引发
TableSchemaException:在过程中引发任何错误
field.constraints
字段约束
返回
dict:字段约束字典
field.descriptor
字段描述符
返回
dict:描述符
field.format
字段格式
返回
str:字段格式
field.missing_values
字段缺失值
返回
str[]:缺失值
字段名
字段名称
返回
str:字段名称
field.required
字段是否必填
返回
bool:如果必填则为真
field.schema
如果字段属于某个模式,则返回模式实例
返回
Schema:字段的模式
field.type
字段类型
返回
str:字段类型
field.cast_value
field.cast_value(value, constraints=True)
根据字段类型和格式转换给定值。
参数
- value (any):要转换的字段值
- constraints (bool/str[]):获取约束配置 - 可以设置为 true 以禁用约束检查 - 可以是一个约束数组以进行检查,例如 ['minimum', 'maximum']
引发
TableSchemaException:在过程中引发任何错误
返回
any:返回转换后的值
field.test_value
field.test_value(value, constraints=True)
测试值是否符合字段。
参数
- value (any):要转换的字段值
- constraints (bool/str[]):约束配置
返回
bool:返回值是否符合字段
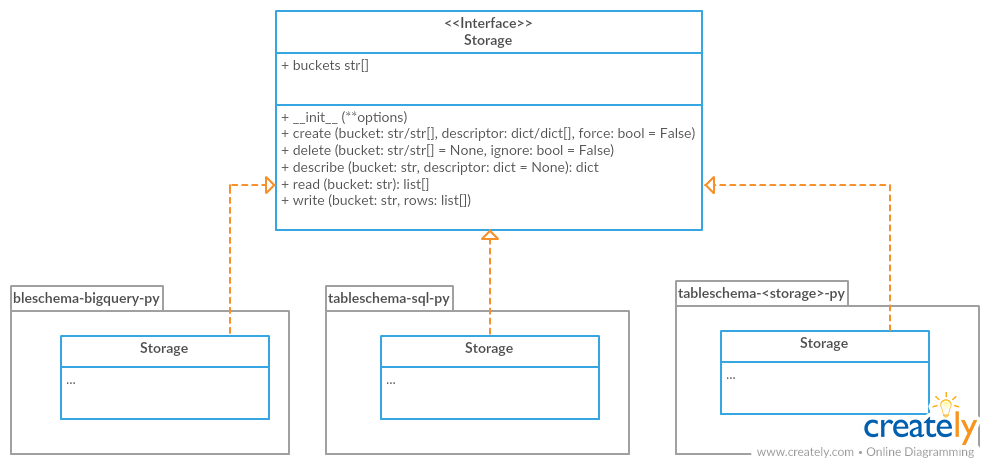
Storage
Storage(self, **options)
存储工厂/接口
对于用户
使用
Storage.connect来实例化存储
对于具体存储实例的创建,tableschema.Storage 提供了一个统一的工厂方法 connect(它底层使用插件系统)
# pip install tableschema_sql
from tableschema import Storage
storage = Storage.connect('sql', **options)
storage.create('bucket', descriptor)
storage.write('bucket', rows)
storage.read('bucket')
对于集成者
该库包含实现表格 Storage 的接口声明。该接口允许使用不同的数据存储系统,如与 tableschema.Table 类(加载/保存)一起使用的 SQL,以及数据包级别
实现者必须遵循 tableschema.Storage 接口来编写自己的存储后端。具体的存储后端可以包括针对具体存储系统的特定功能。有关如何将自定义存储插件集成到工作流程中,请参阅下方的 plugins。
storage.buckets
返回存储桶名称列表。
“桶”是一个特殊术语,其含义几乎与“表”相同。您应将“桶”视为存储在“存储”中的“表”。
引发
exceptions.StorageError:在任何错误上抛出
返回
str[]:返回桶名称列表
storage.connect
storage.connect(name, **options)
根据存储名称创建表格 storage。
此方法为静态:
Storage.connect()
参数
- name (str):存储名称,例如
sql - options (dict):具体存储选项
引发
StorageError:在任何错误上抛出
返回
Storage:返回 Storage 实例
storage.create
storage.create(bucket, descriptor, force=False)
创建一个/多个桶。
参数
- bucket (str/list):桶名称或桶名称列表
- descriptor (dict/dict[]):模式描述符或描述符列表
- force (bool):是否删除并重新创建已存在的桶
引发
exceptions.StorageError:在任何错误上抛出
storage.delete
storage.delete(bucket=None, ignore=False)
删除一个/多个/所有桶。
参数
- bucket (str/list/None):要删除的桶名称或桶名称列表。如果
None,则删除所有桶 - descriptor (dict/dict[]):模式描述符或描述符列表
- ignore (bool):在删除不存在的桶时不要抛出错误
引发
exceptions.StorageError:在任何错误上抛出
storage.describe
storage.describe(bucket, descriptor=None)
获取/设置桶的 Table Schema 描述符
参数
- bucket (str):桶名称
- descriptor (dict/None):要设置的方案描述符
引发
exceptions.StorageError:在任何错误上抛出
返回
dict:返回 Table Schema 描述符
storage.iter
storage.iter(bucket)
返回基于此桶模式的类型值迭代器。
参数
- bucket (str):桶名称
引发
exceptions.StorageError:在任何错误上抛出
返回
list[]:生成数据行
storage.read
storage.read(bucket)
根据此桶的模式读取类型值。
参数
- bucket (str):桶名称 抛出
exceptions.StorageError:在任何错误上抛出 返回
list[]:返回数据行
storage.write
storage.write(bucket, rows)
此方法将数据行写入 storage。
它应将不支持的数据类型的值内部存储为字符串(例如 csv 所做的那样)。
参数
- bucket (str):桶名称
- rows (list[]):要写入的数据行
引发
exceptions.StorageError:在任何错误上抛出
validate
validate(descriptor)
验证描述符
参数
- dict:描述符
引发
ValidationError:在验证错误上
返回
bool:True
infer
infer(source,
headers=1,
limit=100,
confidence=0.75,
missing_values=[''],
guesser_cls=None,
resolver_cls=None,
**options)
推断源模式。
参数
- source (any):源,如路径、URL 或内联数据
- headers (int/str[]):标题行数或标题列表
- confidence (float):允许多少转换错误(作为比例,介于 0 和 1 之间)
- missing_values (str[]):缺失值列表(默认
['']) - guesser_cls (class):您可以通过提供类型猜测和类型解析类来实现推断策略 [实验性]
- resolver_cls (class):您可以通过提供类型猜测和类型解析类来实现推断策略 [实验性]
引发
TableSchemaException:在过程中引发任何错误
返回
dict:返回模式描述符
FailedCast
FailedCast(self, value)
包装原始数据字段值,该值未能正确转换。
FailedCast 允许进行进一步处理/生成值,但仍能在消费端区分未转换的值。
将属性访问和基本丰富比较方法委托给底层对象。支持默认用户定义类的可哈希性,即基于对象标识(而不是基于包装的值)可哈希。
参数
- value (any):值
DataPackageException
DataPackageException(self, message, errors=[])
所有 DataPackage/TableSchema 异常的基类。
如果有多个错误,可以从中读取异常对象
try:
# lib action
except DataPackageException as exception:
if exception.multiple:
for error in exception.errors:
# handle error
datapackageexception.errors
嵌套错误列表
返回
DataPackageException[]:嵌套错误列表
datapackageexception.multiple
是否为嵌套异常
返回
bool:是否为嵌套异常
TableSchemaException
TableSchemaException(self, message, errors=[])
所有 TableSchema 异常的基类。
LoadError
LoadError(self, message, errors=[])
所有加载错误。
ValidationError
ValidationError(self, message, errors=[])
所有验证错误。
CastError
CastError(self, message, errors=[])
所有值转换错误。
IntegrityError
IntegrityError(self, message, errors=[])
所有完整性错误。
UniqueKeyError
UniqueKeyError(self, message, errors=[])
唯一键约束违反(CastError 子类)
RelationError
RelationError(self, message, errors=[])
所有关系错误。
UnresolvedFKError
UnresolvedFKError(self, message, errors=[])
未解决的引用外键错误(RelationError 子类)。
StorageError
StorageError(self, message, errors=[])
所有存储错误。
Experimental
此 API 是实验性的,未来可能更改/删除
存在一个实验性的环境变量 TABLESCHEMA_PRESERVE_MISSING_VALUES,如果设置,将影响数据转换的工作方式。
默认情况下,缺失值解析为 None 值。当此标志设置时,缺失值将原样传递。例如
missing_values.py
from tableschema import Field
field = Field({'type': 'number'}, missing_values=['-'])
print(field.cast_value('3'))
print(field.cast_value('-'))
以不同模式运行此脚本
$ python missing_values.py
3
None
$ TABLESCHEMA_PRESERVE_MISSING_VALUES=1 python missing_values.py
3
-
这些标志会影响所有基于 tableschema 的库 API 和软件。例如,数据包管道
$ TABLESCHEMA_PRESERVE_MISSING_VALUES=1 dpp run ./my_pipeline
贡献
推荐的开始方式是创建并激活一个项目虚拟环境。将安装包和开发依赖项安装到活动环境
$ make install
运行测试并执行代码检查和覆盖率
$ make test
变更日志
这里仅描述了破坏性和最重要的更改。所有发布版本的完整更改日志和文档可以在格式良好的 提交历史 中找到。
v1.20
- 添加了 --json 标志到 CLI (#287)
v1.19
- 在推断中猜测字段名称时去重
v1.18
- 发布
field.ERROR/cast_function/check_functions
v1.17
- 添加了
schema.missing_values和field.missing_values
v1.16
- 修复了解析
geopoint的方式- 作为字符串,它可以有 3 种形式("default","array","object"),但是
- 作为原生对象,它只能是一个列表/元组
v1.15
- 添加了一个实验性的
TABLESCHEMA_PRESERVE_MISSING_VALUES环境变量标志
v1.14
- 允许为
table.infer和infer提供自定义猜测器和解析器
v1.13
- 将
missing_values参数添加到infer函数 (#269)
v1.12
- 支持对 table.iter/read 的可选自定义异常处理 (#259)
v1.11
- 为
field.cast_value添加了preserve_missing_values参数
v1.10
- 添加了在读取时检查表完整性的功能
v1.9
- 实现了
table.size和table.hash属性
v1.8
- 添加了
table.index_foreign_keys_values并改进了外键检查性能
v1.7
- 添加了
field.schema属性
v1.6
- 在
strict模式下,如果字段构造存在问题,则抛出异常
v1.5
- 允许为模式推断提供自定义猜测器和解析器
v1.4
- 添加了
schema.update_field方法
v1.3
- 支持没有时间的时间戳日期转换
v1.2
- 支持类似于 1.0 的浮点数进行整数转换
v1.1
- 为
infer添加了confidence参数
v1.0
- 该库已基于Frictionless Data规范v1重置 - https://frictionlessdata.io/specs/table-schema/
项目详情
tableschema-1.20.11.tar.gz 的散列值
| 算法 | 哈希摘要 | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 89cd4e6cf95a7d7384eaa1594622fe1ce0a887a71ea9da80c8f040a473e5943e |
|
| MD5 | eeb98962943d9ab1d74a1c167a137d13 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | f41b0d5bb28b910f447beb2f7b27ca4217d8e6db43993466de437c82e77e8332 |
tableschema-1.20.11-py2.py3-none-any.whl 的哈希值
| 算法 | 哈希摘要 | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 6e041406c0ee95e9d4621e7548d41a9d6b75829dd8597b02cb07791f790992fe |
|
| MD5 | c5ec75c518859506f6a57e5b6c40a19c |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 5b770b19cd56c2b9c8a6c753a18ee2860a8b140a61a46f83bcd9971c4a7f7f9d |