Notion.so的非官方Python API客户端
项目描述
notion-py
Notion.so API v3的非官方Python 3客户端。
- 面向对象的接口(将数据库表映射到Python类/属性)
- 在内部Notion格式和适当的Python对象之间自动转换
- 在统一的数据存储中缓存数据 (注意:磁盘缓存现在默认禁用;要启用,请在初始化
NotionClient时添加enable_caching=True) - 实时双向数据绑定(更改Python对象 -> 更新Notion UI,反之亦然) (注意:Notion->Python的自动更新目前损坏,因此默认禁用;在同时修复监控期间,调用
my_block.refresh()以更新) - 用于响应Notion变化(例如,触发操作、更新另一个API等)的回调系统
在Jamie的博客上了解更多关于Notion和Notion-py的信息
使用说明
快速入门
注意:notion-py的最新版本需要Python 3.5或更高版本。
pip安装notion
from notion.client import NotionClient
# Obtain the `token_v2` value by inspecting your browser cookies on a logged-in (non-guest) session on Notion.so
client = NotionClient(token_v2="<token_v2>")
# Replace this URL with the URL of the page you want to edit
page = client.get_block("https://www.notion.so/myorg/Test-c0d20a71c0944985ae96e661ccc99821")
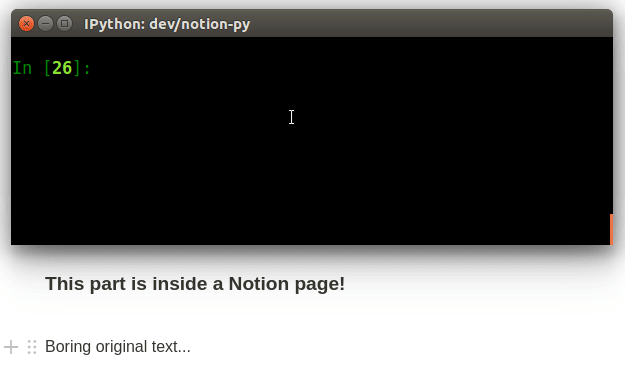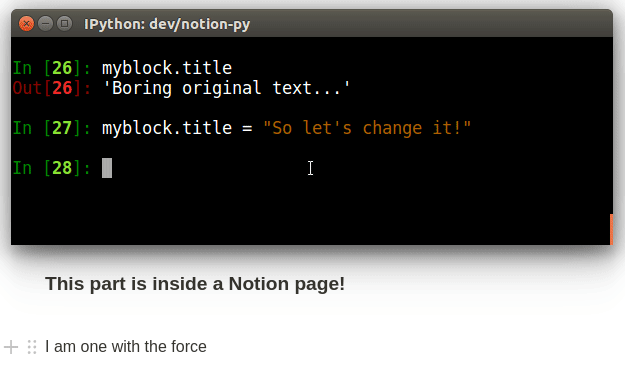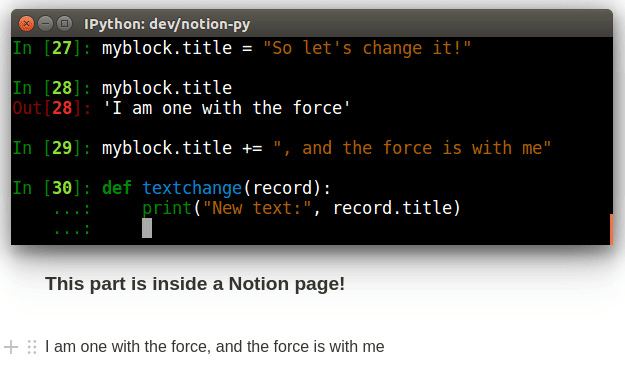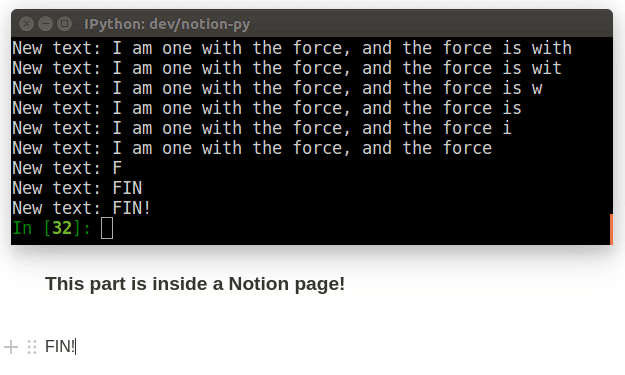
print("The old title is:", page.title)
# Note: You can use Markdown! We convert on-the-fly to Notion's internal formatted text data structure.
page.title = "The title has now changed, and has *live-updated* in the browser!"
概念和笔记
- 我们将Notion数据库中的表格映射到Python类(继承自
Record),每个类的实例代表一条特定的记录。一些字段(如上述示例中的title)已被映射到模型属性,使得记录的读写变得简单快捷。其他字段可以通过get方法读取,通过set方法写入,但此时需要确保与内部结构完全匹配。 - 我们目前支持的表格包括block(通过
Block类及其子类,对应不同的type),space(通过Space类),collection(通过Collection类),collection_view(通过CollectionView及其子类),以及notion_user(通过User类)。 - 所有表格的数据都存储在中央的
RecordStore中,其中Record实例不存储内部状态,而始终引用中央的RecordStore中的数据。许多API操作返回大量关联记录的更新版本,我们使用这些更新来更新存储,因此Record实例中的数据有时会在未明确请求的情况下更新。您也可以在Record上调用refresh方法来触发更新,或者将force_update传递给像get这样的方法。 - API对大多数数据没有严格的验证,因此请注意保持Notion期望的结构。您可以通过不带参数调用
myrecord.get()来查看记录的完整内部结构。 - 当您调用
client.get_block时,您可以传递ID或页面的URL。请注意,页面本身只是blocks,页面上的所有内容块也是如此。您可以通过点击块上下文菜单中的“复制链接”来获取页面内块的URL,并将其作为参数传递给get_block。
更新记录
我们保留所有通过的数据的本地缓存。当您在Record上引用属性时,我们首先在缓存中查找以检索值。如果没有找到,则从服务器检索。您还可以通过在Record上调用refresh方法来手动刷新Record的数据。默认情况下(除非我们使用monitor=False实例化NotionClient),我们还订阅了长轮询更新,因此这些Records的本地缓存数据应在服务器上的数据更改后不久自动更新。长轮询在后台守护线程中发生。
示例:遍历块树
for child in page.children:
print(child.title)
print("Parent of {} is {}".format(page.id, page.parent.id))
示例:添加新节点
from notion.block import TodoBlock
newchild = page.children.add_new(TodoBlock, title="Something to get done")
newchild.checked = True
示例:删除节点
# soft-delete
page.remove()
# hard-delete
page.remove(permanently=True)
示例:创建嵌入式内容类型(iframe、视频等)
from notion.block import VideoBlock
video = page.children.add_new(VideoBlock, width=200)
# sets "property.source" to the URL, and "format.display_source" to the embedly-converted URL
video.set_source_url("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oHg5SJYRHA0")
示例:创建新的嵌入式集合视图块
collection = client.get_collection(COLLECTION_ID) # get an existing collection
cvb = page.children.add_new(CollectionViewBlock, collection=collection)
view = cvb.views.add_new(view_type="table")
# Before the view can be browsed in Notion,
# the filters and format options on the view should be set as desired.
#
# for example:
# view.set("query", ...)
# view.set("format.board_groups", ...)
# view.set("format.board_properties", ...)
示例:移动块
# move my block to after the video
my_block.move_to(video, "after")
# move my block to the end of otherblock's children
my_block.move_to(otherblock, "last-child")
# (you can also use "before" and "first-child")
示例:订阅更新
(注意:Notion到Python的自动更新目前损坏,因此默认禁用;在修复监控的同时,调用my_block.refresh()以更新)
我们可以“监视”一个Record,以便在它更改时接收回调。结合基于长轮询的记录实时更新,这允许“响应式”设计,其中我们的本地应用程序中的操作可以由与Notion界面的交互触发。
# define a callback (note: all arguments are optional, just include the ones you care about)
def my_callback(record, difference):
print("The record's title is now:" record.title)
print("Here's what was changed:")
print(difference)
# move my block to after the video
my_block.add_callback(my_callback)
示例:处理数据库,即“集合”(表格、板等)
以下是它们如何协同工作
- 主容器块:
CollectionViewBlock(内联)/CollectionViewPageBlock(全页)Collection(包含模式,且是数据库行本身的父级)CollectionRowBlockCollectionRowBlock- ...(更多数据库记录)
CollectionView(包含关于每个特定视图的过滤器/排序等)
注意:为了方便起见,我们自动根据在Collection中定义的模式将数据库“列”(即属性)映射到CollectionRowBlock实例的getter/setter属性上。属性名称是列名的“slugified”版本。因此,如果您有一个名为“Estimated value”的列,您可以通过myrowblock.estimated_value来读写它。可能进行一些基本验证,并将其转换为适当的内部格式。对于类型为“Person”的列,我们期望一个User实例或它们的列表,对于“Relation”,我们期望一个Block子类的单一实例或列表。
# Access a database using the URL of the database page or the inline block
cv = client.get_collection_view("https://www.notion.so/myorg/8511b9fc522249f79b90768b832599cc?v=8dee2a54f6b64cb296c83328adba78e1")
# List all the records with "Bob" in them
for row in cv.collection.get_rows(search="Bob"):
print("We estimate the value of '{}' at {}".format(row.name, row.estimated_value))
# Add a new record
row = cv.collection.add_row()
row.name = "Just some data"
row.is_confirmed = True
row.estimated_value = 399
row.files = ["https://www.birdlife.org/sites/default/files/styles/1600/public/slide.jpg"]
row.person = client.current_user
row.tags = ["A", "C"]
row.where_to = "https://learningequality.org"
# Run a filtered/sorted query using a view's default parameters
result = cv.default_query().execute()
for row in result:
print(row)
# Run an "aggregation" query
aggregations = [{
"property": "estimated_value",
"aggregator": "sum",
"id": "total_value",
}]
result = cv.build_query(aggregate=aggregate_params).execute()
print("Total estimated value:", result.get_aggregate("total_value"))
# Run a "filtered" query (inspect network tab in browser for examples, on queryCollection calls)
filter_params = {
"filters": [{
"filter": {
"value": {
"type": "exact",
"value": {"table": "notion_user", "id": client.current_user.id}
},
"operator": "person_contains"
},
"property": "assigned_to"
}],
"operator": "and"
}
result = cv.build_query(filter=filter_params).execute()
print("Things assigned to me:", result)
# Run a "sorted" query
sort_params = [{
"direction": "descending",
"property": "estimated_value",
}]
result = cv.build_query(sort=sort_params).execute()
print("Sorted results, showing most valuable first:", result)
注意:您可以组合filter、aggregate和sort。通过在Notion中设置复杂的视图并检查完整的查询cv.get("query2"),可以查看更多查询示例。
您还可以在烟雾测试运行器中看到更多操作示例。运行它使用
python run_smoke_test.py --page [YOUR_NOTION_PAGE_URL] --token [YOUR_NOTION_TOKEN_V2]
示例:锁定/解锁页面
from notion.client import NotionClient
# Obtain the `token_v2` value by inspecting your browser cookies on a logged-in session on Notion.so
client = NotionClient(token_v2="<token_v2>")
# Replace this URL with the URL of the page or database you want to edit
page = client.get_block("https://www.notion.so/myorg/Test-c0d20a71c0944985ae96e661ccc99821")
# The "locked" property is available on PageBlock and CollectionViewBlock objects
# Set it to True to lock the page/database
page.locked = True
# and False to unlock it again
page.locked = False
示例:为多账户用户设置当前用户
from notion.client import NotionClient
client = NotionClient(token_v2="<token_v2>")
# The initial current_user of a multi-account user may be an unwanted user
print(client.current_user.email) # → not_the_desired@email.co.jp
# Set current_user to the desired user
client.set_user_by_email('desired@email.com')
print(client.current_user.email) # → desired@email.com
# You can also set the current_user by uid.
client.set_user_by_uid('<uid>')
print(client.current_user.email) # → desired@email.com
快速插入:Learning Equality需要您的支持!
如果您想支持notion-py开发,请考虑向我的开源非营利组织Learning Equality捐款,因为当我不在notion-py工作时,这通常意味着我正在埋头进行全球教育工作的筹款(将如Khan Academy等资源带到没有互联网的社区)。COVID进一步加剧了需求,超过十亿的孩子被困在家中,其中一半以上没有进行远程学习所需的连接性。您现在也可以通过GitHub Sponsors来支持我们的工作!
相关项目
- md2notion:将Markdown文件导入到Notion
- notion-export-ics:将Notion数据库导出到ICS日历文件
- notion-tqdm:在Notion中显示进度条,类似于tqdm
TODO
- 分层克隆页面
- 防抖缓存保存?
- 支持在Markdown转换中内联“用户”和“页面”链接,以及提醒
- 支持更新/创建集合模式的功能
- 支持更新/创建集合_view查询的功能
- 支持轻松管理页面权限
- WebSocket支持实时块缓存更新
- “渲染全页为Markdown”模式
- “从HTML导入页面”模式
项目详情
下载文件
下载您平台的文件。如果您不确定选择哪个,请了解有关安装包的更多信息。