最小化访问GUI、TUI、CLI和配置
项目描述
Mininterface – 访问GUI、TUI、CLI和配置文件
编写程序核心,无需担心输入/输出。
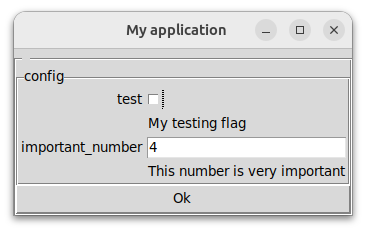
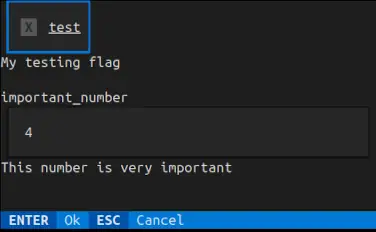
查看代码,它意外地很短,可以显示这样的窗口或其文本回退。
from dataclasses import dataclass
from mininterface import run
@dataclass
class Env:
""" This calculates something. """
my_flag: bool = False
""" This switches the functionality """
my_number: int = 4
""" This number is very important """
if __name__ == "__main__":
env = run(Env, prog="My application").env
# Attributes are suggested by the IDE
# along with the hint text 'This number is very important'.
print(env.my_number)
内容
您有了CLI
这是您需要的所有代码。没有外部依赖性强加的长代码块。除了GUI/TUI之外,您还收到了强大的YAML配置CLI解析。
$ ./hello.py
usage: My application [-h] [--test | --no-test] [--important-number INT]
This calculates something.
╭─ options ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ -h, --help show this help message and exit │
│ --test, --no-test My testing flag (default: False) │
│ --important-number INT This number is very important (default: 4) │
╰────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
您有了配置文件管理
加载配置文件轻而易举。将 program.py 与 program.yaml 一起放置,并在其中放置一些参数。它们无缝地作为默认值采用。
my_number: 555
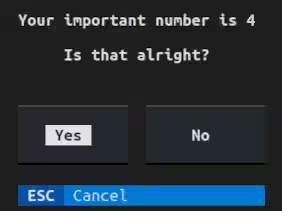
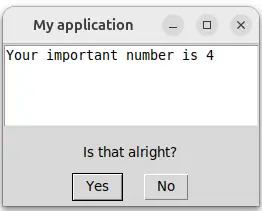
您有了对话框
查看几个有用的方法来处理用户对话框。在这里,我们将界面绑定到将stdout直接重定向到窗口的 with 语句。
with run(Env) as m:
print(f"Your important number is {m.env.my_number}")
boolean = m.is_yes("Is that alright?")
背景
在 tyro argparse 替代品和 tkinter_form 之间的包装器,后者将字典转换为GUI。
编写一个简单而实用的程序可能只需要十五分钟。添加一个命令行界面来指定参数并不会增加太多开销。但是围绕它构建一个简单的GUI呢?需要好几个小时!几个小时都花在研究GUI库上,纳闷为什么Python桌面应用程序生态系统落后于网络世界那么远。你所需要的只是一个可以通过点击窗口进行验证的几个输入字段...你不值得为了定义一些可编辑的字段而添加数百行代码。Mininterface就是来帮忙的。
你的程序所需配置变量都存储在舒适的数据类中。写得更少!tyro的语法不需要任何开销(与它的argparse替代品相比)。你只需注释一个类属性,附加一个简单的文档字符串,就可以得到一个完整功能的应用程序
- 通过
program.py --help调用它来显示完整帮助。 - 在CLI中使用任何标志:
program.py --my-flag会将env.my_flag设置为True。 - 主要好处:无需参数直接作为
program.py启动,即可获得一个带有所有可编辑标志的完整工作窗口。 - 在远程机器上运行?自动回退到文本界面。
安装
通过PyPi的单个命令安装。
pip install mininterface
文档
在https://cz-nic.github.io/mininterface/查看文档概述。
示例
复杂的数据类。
from typing import Annotated
from dataclasses import dataclass
from mininterface.validators import not_empty
from mininterface import run, Tag, Validation
@dataclass
class NestedEnv:
another_number: int = 7
""" This field is nested """
@dataclass
class Env:
nested_config: NestedEnv
mandatory_str: str
""" As there is not default value, you will be prompted automatically to fill up the field """
my_number: int | None = None
""" This is not just a dummy number, if left empty, it is None. """
my_string: str = "Hello"
""" A dummy string """
my_flag: bool = False
""" Checkbox test """
my_validated: Annotated[str, Validation(not_empty)] = "hello"
""" A validated field """
m = run(Env, title="My program")
# See some values
print(m.env.nested_config.another_number) # 7
print(m.env)
# Env(nested_config=NestedEnv(another_number=7), my_number=5, my_string='Hello', my_flag=False, my_validated='hello')
# Edit values in a dialog
m.form()
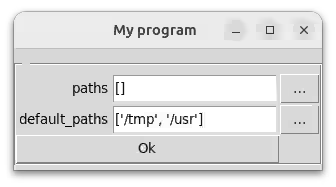
带有路径的表单
我们有一个包含一些路径的字典。下面是它的样子。
from pathlib import Path
from mininterface import run, Tag
m = run(title="My program")
my_dictionary = {
"paths": Tag("", annotation=list[Path]),
"default_paths": Tag([Path("/tmp"), Path("/usr")], annotation=list[Path])
}
# Edit values in a dialog
m.form(my_dictionary)
项目详情
下载文件
下载适用于您平台的文件。如果您不确定选择哪个,请了解有关安装包的更多信息。
源分布
mininterface-0.6.1.tar.gz (35.1 kB 查看散列)
构建分布
mininterface-0.6.1-py3-none-any.whl (43.7 kB 查看散列)
关闭
mininterface-0.6.1.tar.gz的散列
| 算法 | 散列摘要 | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 750f9c025764ea8ec4e6bb5eb14e1928dddaf57ad41449811f123e7a98369708 |
|
| MD5 | 083d211c452ad493774ffd62fe198444 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 246944b79743fe956fc4eee196b267382ba90ecae215e699135be42df48cb009 |
关闭
mininterface-0.6.1-py3-none-any.whl的散列
| 算法 | 散列摘要 | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | a6c144d2477ef031580b2a4626c60e0d0de0d1fa6d0ce594dbc90bfb0a9a774c |
|
| MD5 | 2abcda36f6d348a4b1048682f7a0fe37 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 021416530c7d6cf7937cbde600411478d7e108ca6f68925b2ae422b3791ef859 |